Network Automation What is network automation?
Network automation uses intelligent software to execute specified tasks that are often considered tedious, time-consuming, or complex. It can be implemented during design, configuration, deployment, and ongoing network operations for improved IT efficiency and resourcing, greater network visibility and control, and a more responsive and proactive response to critical issues.
Time to read: 6 minutes 12 seconds | Updated: October 31, 2025
Table of Contents
Network automation explained
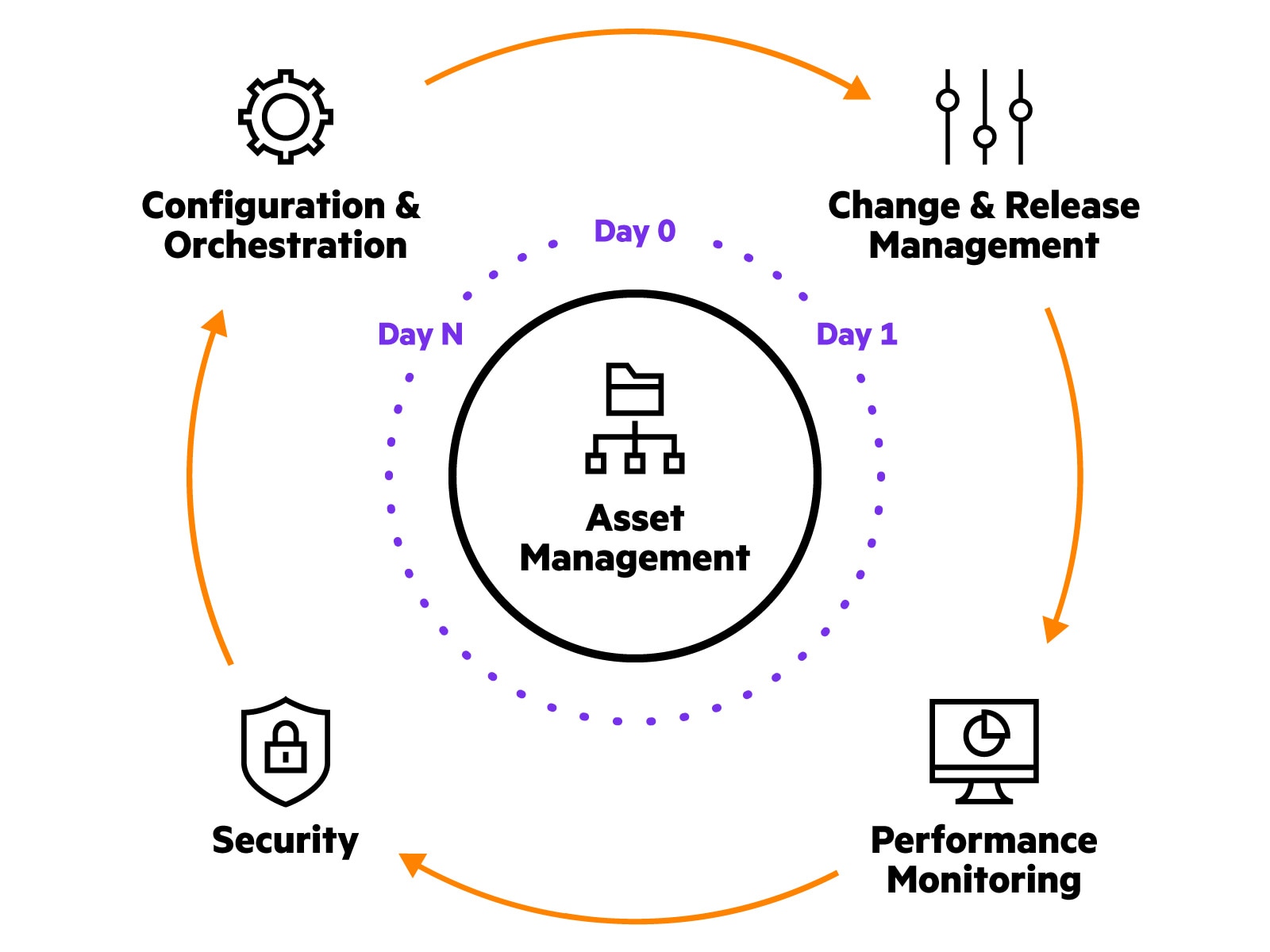
Network automation simplifies operations and creates a secure, high-performance, always-on network from Day 0 through Day N. With the appropriate network services in place, several key areas of operations can be optimized, including:
- Asset management that provides better visibility and control with a unified view of the entire network (from access points, network switches, and gateways to clients and applications) and facilitates lifecycle management including licensing.
- Configuration and orchestration that enables zero touch provisioning, deployment, and configuration changes for new and existing network devices across campus, data center and remote sites. When cloud-based services platforms like HPE Aruba Networking Central are used, complex CLI programming and scripts are replaced with centralized policies, further reducing the need for IT intervention.
- Change and release management that streamlines regular software upgrades with zero downtime, supports rollback to the previous state of network devices, and can implement role-based access control (RBAC) to track and ensure that only authorized users have access for network modifications.
- AI-powered performance monitoring and troubleshooting that proactively detects network, security and application performance issues using dynamic baselines and resolves them with machine learning-based recommendations before users are impacted. Automated SLAs are established through peer comparisons. Instant alerts are triggered upon breaching these predefined thresholds.
- Improved security by ensuring complete visibility, authentication, and enforcement of consistent network and security policies that seamlessly adapt to user and device behavior, regardless of the location. This approach involves continuous monitoring and addressing of security and compliance requirements, aligning with the principles of a zero trust model. Network automation also minimizes human errors in configurations across multiple deployments, ensuring network uptime and security.
- HPE Aruba Networking provides network automation via its cloud native, microservices-based platform, Central. Please refer to the table below for details.
Why is network automation important?
Network automation can streamline operations, improve efficiency, and reduce human error:
- TechTarget states that manual configuration using CLI, scripts, or complex ACLs has proven ineffective, contributing to 90% of network issues.
- ZK Research reports a network engineer spends 10 hours a week on average to find and fix Wi-Fi problems, and 60% still use packet capture as their primary troubleshooting tool.
What are the benefits of network automation?
- Enhanced network resiliency by proactively tracking anomalies and triggering alerts, enabling IT teams to introduce AIOps in the network and stay ahead with comprehensive insights into performance, utilization, security, and resource allocation, resulting in faster issue resolution and continuous business operations as compared to manual techniques.
- Introduction of AIOps by integrating machine learning and big data techniques into microservices-based cloud-native networking platforms for proactive insights, recommendations and closed loop automation. Network issues that previously demanded days or weeks of troubleshooting such as coverage hole identification or port flapping can now be discovered and addressed quickly.
- Increased operational efficiency by triggering automated workflows using predefined rules, cutting down on the time spent on repetitive tasks, and enhancing agility and network performance while preventing human errors.
- Enhanced network visibility and control by offering comprehensive insights into the entire network and flexibility for IT admins to exert precise network control and adapt as required.
- Extend operations to IoT by providing unified visibility, network monitoring and insights to BLE, Zigbee and other IP and non-IP based IoT devices without requiring any specialized components or skills.
- Minimized security risks by automating critical tasks such as software updates, patch management, and access control as per user roles. Automated network configuration ensures consistency and adherence to all compliance standards.
- Support for sustainability by providing a centralized platform that eliminates the need for multiple management consoles, optimizing networks and IT operations. This efficiency reduces power consumption and resource usage while meeting service level expectations.
Challenges of implementing network automation
- Interoperability and complexity: A mismatch of different features and interfaces and incompatibility with existing devices or other 3rd party systems can cause conflicts, errors, or failures, impacting network performance and security.
- Cost: Some solutions demand premium licenses, specific hardware, or maintenance that can outweigh the potential benefits. Conversely, low-cost network automation tools may compromise quality, reliability, or security.
- Integration: Thoughtful allocation of IT resources is crucial for the seamless adoption of network automation, freeing up capacity for strategic tasks.
- IT skill gap: IT admins may face challenges due to inadequate knowledge and the need to learn new tools and languages (Python, Ansible, or Netconf) can hinder overall efficiency.
The role of artificial intelligence in network automation
AI helps make networks adaptive by delivering predictive insights, recommendations, and actions and can automatically set up service level baselines that are adjusted based on network and user/IoT device behavior. AI plays an important role in network automation in several ways:
- Intent based networking (IBN) for network configuration and management based on business intent instead of complex technical specifications. As an example, network access of suspicious users is revoked based on business intent, reducing the time and resources required to operate the network while significantly increasing network reliability, performance, and security.
- Interactive network operations that can be delivered with large language model (LLM)-based generative AI capabilities to streamline tasks such as documentation retrieval, impact assessment, and troubleshooting, significantly saving time.
- AI-assisted sustainable practices that offers power-saving recommendations to configure APs to power down during low use hours.
How can you automate your network with HPE Aruba Networking Central?
Steps | Use cases | Features |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Identify network devices and assign licenses to them | Asset management |
|
| 2. Design network topology and configure devices | Configuration and orchestration |
|
| 3. Test configuration and perform upgrades without downtime | Change and release management |
|
| 4. Identify and monitor issues before it affects your network | Performance monitoring and troubleshooting |
|
| 5. End-user Digital Experience Monitoring (DEM) | Testing network, SaaS, and web applications |
|
| 6. Identify, authenticate, and provide role-based access policies to clients and devices | Security |
|
| 7. Consume network infrastructure in a subscription-based or flexible consumption model | Network-as-a-service |
|
FAQs
What problem does network automation solve?
With the introduction of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), advanced network automation solutions analyze meta-data and leverage model-driven network programmability to learn network behaviors, deliver predictive analysis, and provide recommendations to network operations teams. These advanced automation solutions can be configured to take remedial action autonomously, providing closed-loop remediation of network issues, sometimes even before they even occur. In doing so, network automation improves operational efficiency, reduces the potential for human error, increases network service availability, and delivers a better customer experience.
What is future of network automation?
Looking ahead, networks of the future will be able to accomplish the following:
- AI and ML-driven networks will learn the intent of network behaviors, deliver predictive analysis, and provide recommendations/remediations.
- Implement automatic service placement and service motion.
- Use advanced probing technology to actively monitor service assurance and adjust traffic flows based on service requirements.
- Provide specific upgrades based on configured services.
- Operate autonomously, with active monitoring and reporting provided to network operators, to verify network performance and behaviors remain aligned to business goals.
The route forward toward an autonomous network relies on telemetry, automation, machine learning, and programming with declarative intent. This future network is called the Self-Driving Network™, an autonomous network that is predictive and adaptive to its environment.
Why is network automation important?
In the era of 5G and cloud, automation is becoming essential for managing converged IP service fabrics at scale. Automation reduces human errors, the most common cause of network performance degradation and downtime, making automated networks more reliable. Service providers and large enterprises can also use automation to reduce time to market, improve customer experiences, and meet growing scalability demands with simplified network operations. The result is greater network efficiency, uptime, and consistency across the board.
How is AI used in network automation?
AI is used for automated collection and normalization of data across network domains and vendors, intelligent root-cause analysis, and alerts about potential performance degradation or equipment malfunctions. It’s particularly useful for understanding anomalies that may impact customer services, often resolving issues before users are affected.
How does network programmability differ from network automation?
To take advantage of automation, networks need to become programmable by supporting new configuration methods such as NETCONF/YANG. A modern cloud-native platform that offers low-code workflow automation and REST APIs will allow organizations to automate processes such as network planning, configuration, compliance verification, service activation, quality verification, performance monitoring, path computation, and closed-loop remediation to improve network efficiency and service performance.
What network automation solutions does HPE Juniper Networking offer?
The HPE Juniper Networking Paragon Automation suite of cloud-native applications automates and manages the entire lifecycle of your network services. Available to run on-premises or in the cloud as a SaaS offering, Paragon Automation helps you plan, orchestrate, assure, and optimize your network services automatically.