
Hybrid Cloud Storage
What is Hybrid Cloud Storage?
Hybrid cloud storage combines on-premises (data center or colo) and public cloud storage resources within an organization’s data landscape via technology that enables data portability. A hybrid cloud strategy enables organizations to leverage on-premises storage and public cloud storage with seamless migration between the two to achieve unprecedented agility, flexibility, and resource optimization across environments.

- Hybrid cloud storage architecture
- Types of hybrid cloud storage
- Data management in hybrid cloud storage
- Advantages and disadvantages of hybrid cloud storage
- Hybrid cloud storage use cases
- Hybrid cloud storage best practices
- HPE leads hybrid cloud storage innovation
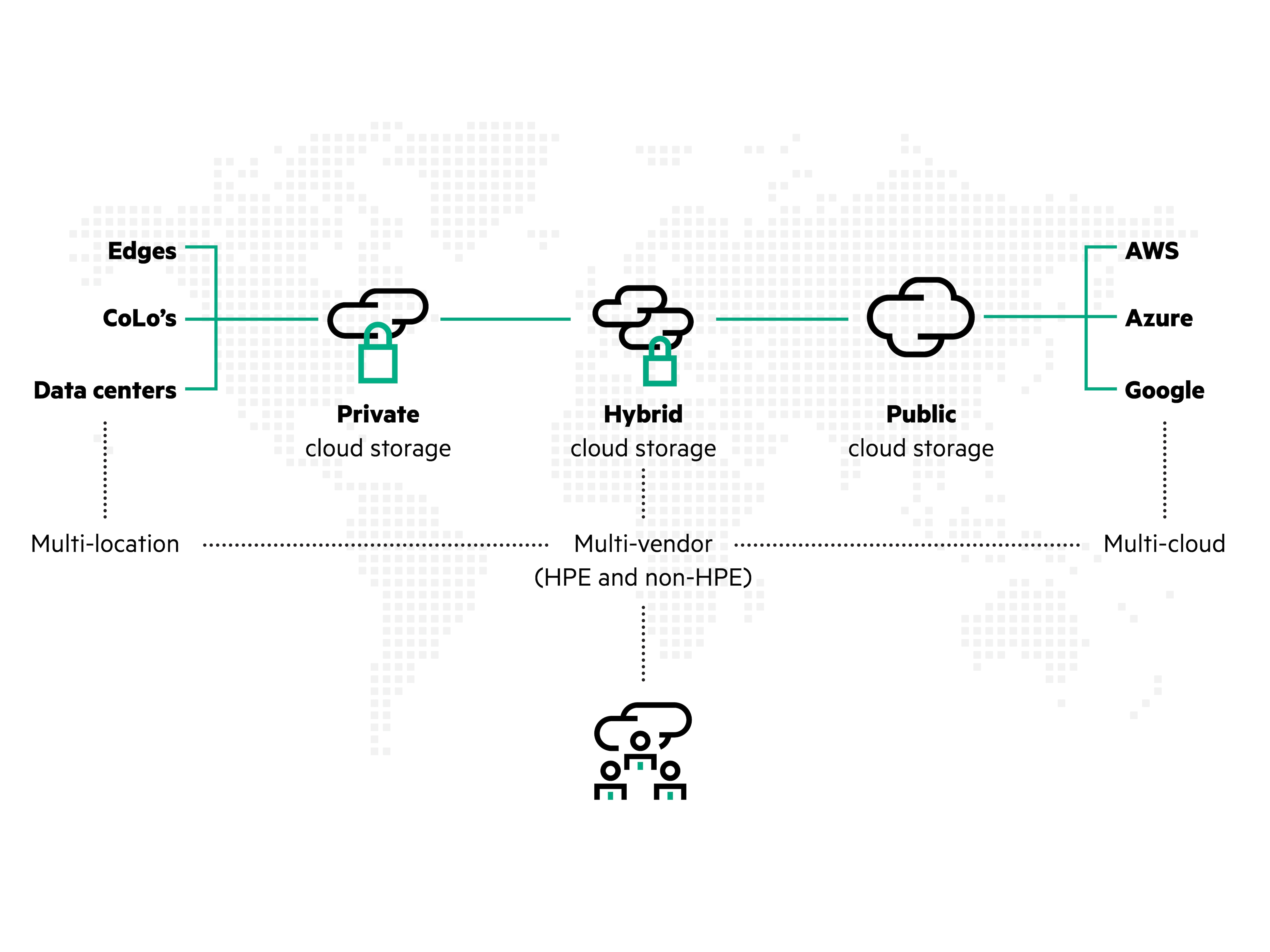
Hybrid cloud storage architecture
Hybrid cloud storage employs on-premises and public cloud storage resources to provide a flexible and scalable storage solution. A hybrid cloud strategy enables organizations to leverage on-premises storage and public cloud storage with seamless migration between the two to achieve unprecedented agility and flexibility across environments.
Hybrid cloud storage is comprised of:
- On-premises storage: The most advanced on-prem storage offerings provide a cloud experience in terms of provisioning workloads and ease of management. Organizations use on-premises storage for sensitive or essential data that needs high performance, low latency, or regulatory compliance.
- Public cloud storage: Cloud service providers such as AWS, Azure, and GCP offer storage capabilities for public cloud storage. Public cloud storage solutions are scalable and offer low cost of entry, typically with pay-as-you-go pricing. These solutions can work well for backup, archive, test/dev, and new initiatives. Hybrid cloud combines on-premises infrastructure and public cloud services. Organizations operate hybrid cloud storage to improve flexibility, performance, and cost by effortlessly migrating data between on-premises and public cloud resources based on changing IT demands.
