Network Segmentation What is Network Segmentation?
Network segmentation is a security practice that divides a network into smaller subnetworks to improve security, reduce traffic congestion, and enhance performance.

- Network segmentation explained
- What are the different types of network segmentation?
- What are the benefits of network segmentation?
- What are the top use cases for network segmentation?
- What is the difference between network segmentation and microsegmentation?
- How does network segmentation enable Zero Trust?
- Network segmentation and HPE Aruba Networking
Network segmentation explained
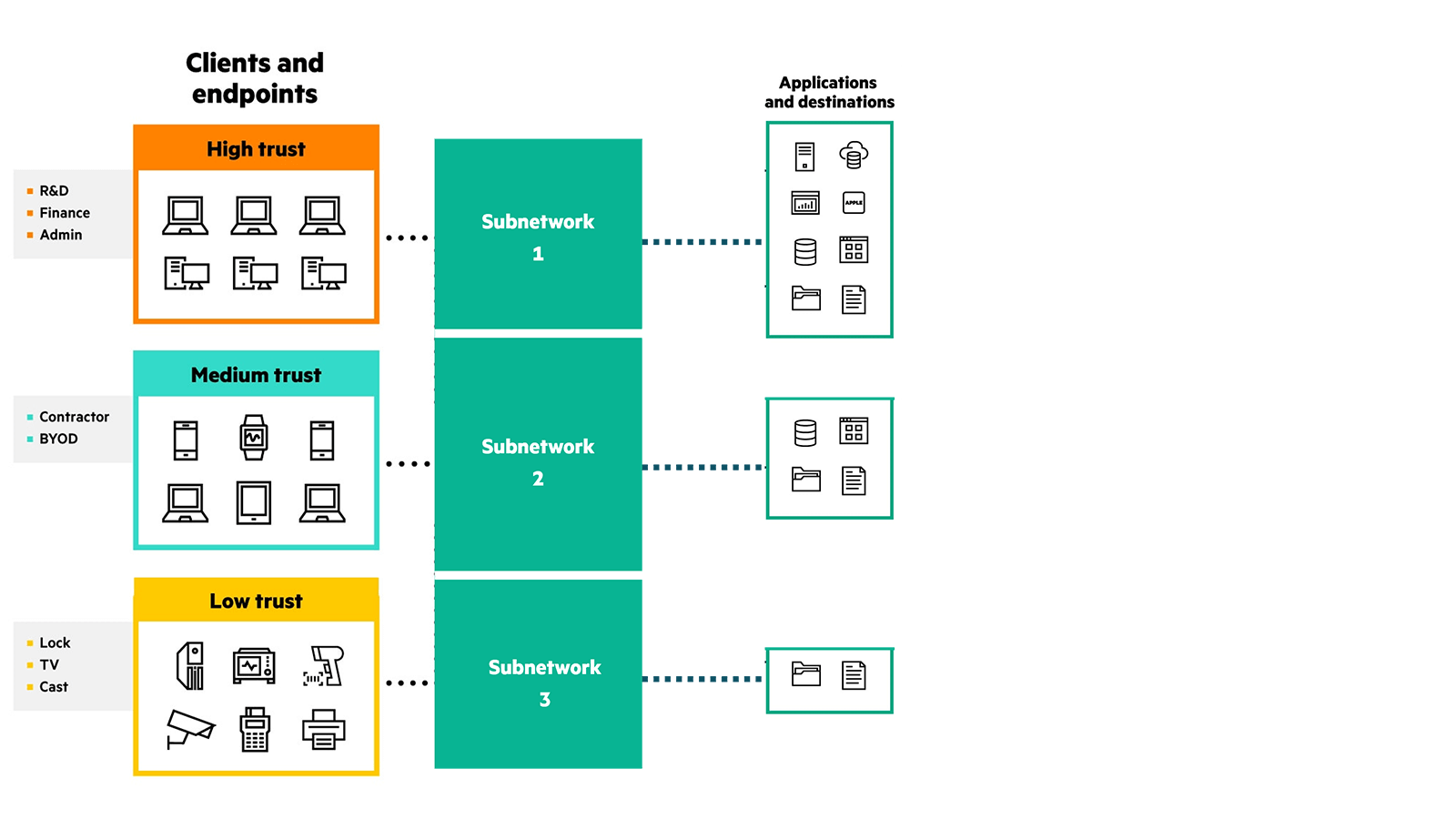
Network segmentation is a security practice of dividing a network into smaller subnetworks, with each dedicated to specific groups of devices, users, or resources. This practice strengthens cybersecurity by controlling traffic flow between subnetworks or segments, thereby containing any potential security breaches within a specific segment and helping to prevent lateral spread of threats. It also improves network performance by isolating critical resources from non-essential workloads.
Network segmentation enhances north-south security by reducing the attack surface and regulating traffic between different segments based on predefined policies. For example, in a large enterprise that provides network access to employees, contractors, and IoT devices, segmentation can enforce security policies on the basis of trust level of connecting devices, preventing IoT devices from accessing sensitive systems, such as financial or HR systems, while prioritizing network resources for employees working with critical resources.