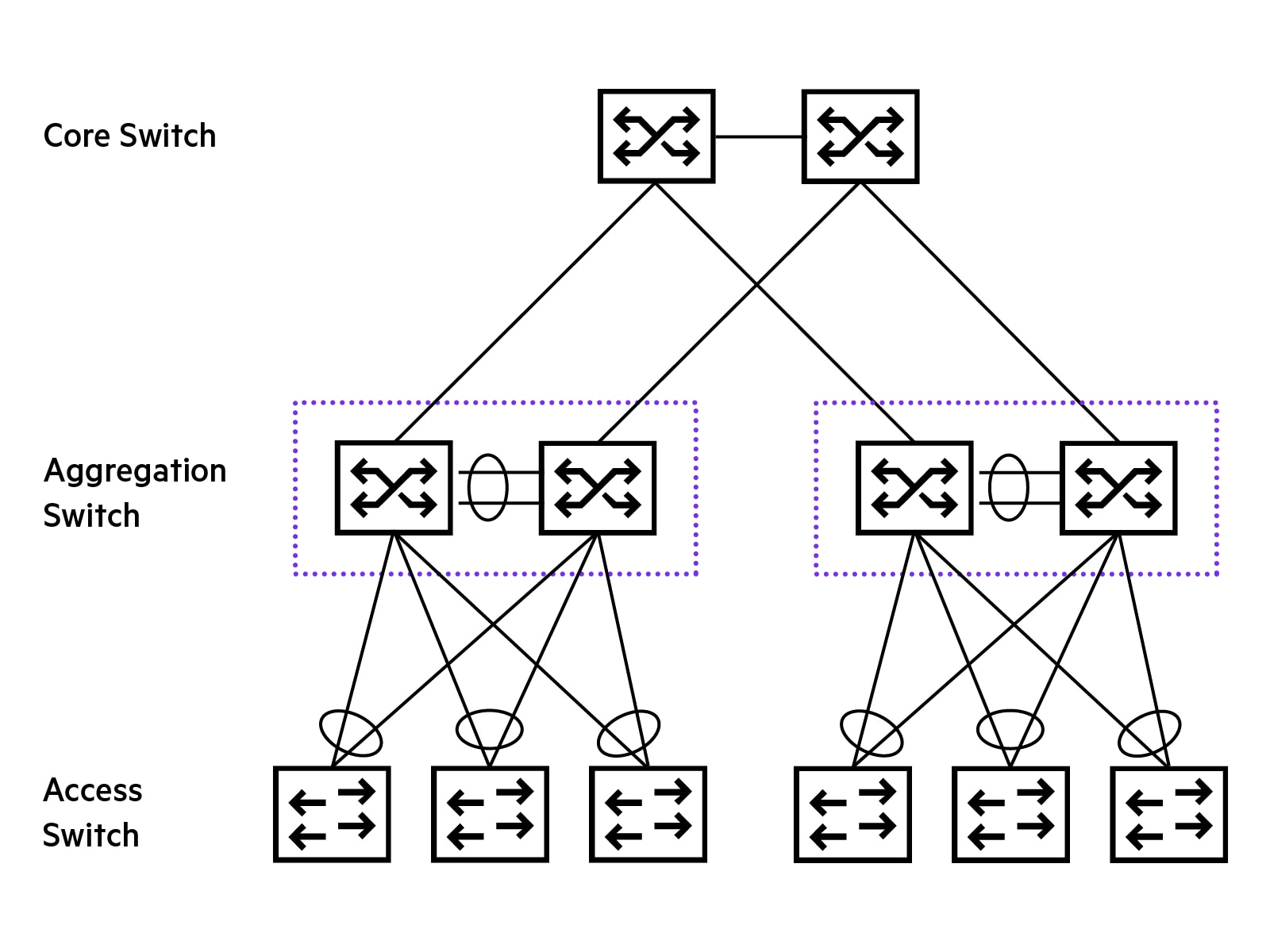
Ethernet switching What is Ethernet switching?
Ethernet switching is a network process that efficiently receives and forwards data, transmitting packets between wired devices and to their intended destination, commonly within a local area network. The equipment that performs this process is called an Ethernet switch (also called a network switch).

- Ethernet switching explained
- IEEE standards for Ethernet switching
- Why Ethernet switching?
- Types of Ethernet switching devices
- How do I choose an Ethernet switching vendor?
- HPE Aruba Networking CX Switches
Ethernet switching explained
Ethernet switching is a network process that efficiently receives and forwards data, transmitting packets across network nodes and between physically connected wired devices to their intended destination, commonly within a local area network.
The equipment that performs this process is called an Ethernet switch (also called a network switch). Ethernet switches transmit packets through physical ports and fiber or copper twisted pair cabling to other devices, like access points (APs), IoT devices, computers, and other network equipment.
To find the correct destination device, an Ethernet switch will often reference and forward a data packet according to its listed destination MAC address—a physical address typically embedded into a device during manufacturing. More sophisticated forms of Ethernet switching can assign and reference IP addresses to devices within the network and use them to apply policies, track flows, and shape traffic to meet IT operational requirements for performance and segmentation.